Ever felt like your business reports are a tangled mess of numbers and charts? Or maybe you get them, but struggle to see how they translate into actual growth for your company? You’re not alone. Business reports are powerful tools, but unlocking their true potential requires knowing how to analyze and interpret them effectively.
This guide will take you on a journey from report-reading rookie to strategic growth guru. We’ll break down the process of analyzing business reports, introduce key techniques, and show you how to translate dry data into actionable insights that propel your business forward.
How Do You Analyze Business Growth?

Business growth analysis is all about understanding where your company stands and where it’s headed. It involves examining key metrics that paint a picture of your financial health, operational efficiency, and market position. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
- Identify Your Goals: What kind of growth are you aiming for? Increased revenue? Market share expansion? Improved customer satisfaction? Defining your goals sets the stage for analyzing relevant metrics.
- Gather Relevant Data: This includes information from your business reports, industry benchmarks, and competitor analysis. Look for trends, patterns, and outliers.
- Analyze the Data: Use various techniques like trend analysis, ratio analysis, and variance analysis to interpret the meaning behind the numbers. Identify areas of strength and weakness.
- Interpret and Draw Conclusions: What does the data tell you about your progress towards goals? Are there any roadblocks hindering growth?
- Formulate Actionable Strategies: Based on your analysis, develop concrete steps to capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, and achieve your growth goals.
What are the 5 Business Analysis Techniques?
Business analysis offers a toolbox filled with techniques to dissect your reports and extract valuable insights. Mastering these techniques will help you transform from being a passive report reader to an active analyst, uncovering hidden gems of information that can fuel your business’ growth.
Here are 5 key techniques to get you started:
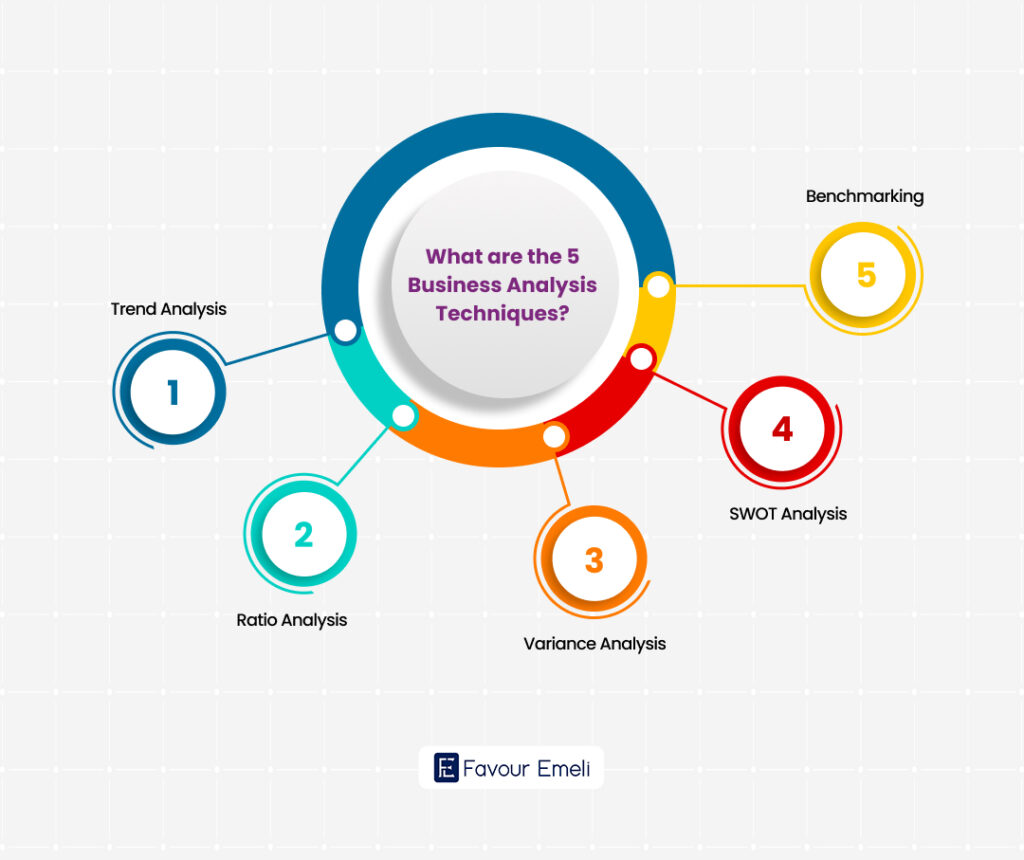
Trend Analysis
This technique involves examining data points over time to identify trends, such as increasing sales or declining customer retention. By spotting trends, you can anticipate future performance and make informed decisions.
Ratio Analysis
This technique involves calculating ratios between different financial statement elements. For example, the current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term debts. Analyzing ratios helps assess your company’s financial health, liquidity, profitability, and efficiency.
Variance Analysis
This technique compares actual results to budgeted or forecasted figures. Analyzing variances helps identify areas where performance has deviated from expectations, allowing you to pinpoint problems and take corrective action.
SWOT Analysis
This strategic planning framework helps you identify your company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. By understanding these internal and external factors, you can develop strategies that leverage your strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats.
Benchmarking
This technique involves comparing your company’s performance metrics to industry standards or competitors. Benchmarking helps you identify areas where you excel or fall short, allowing you to learn from industry best practices and improve your competitive edge.
Also, see this: 9+ Best Business Books Every Entrepreneur Should Have
What are the 5 Main Parts of a Business Report?
Business reports come in various shapes and sizes, but most share a common core structure. Understanding these sections means effective analysis for your business or company’s growth:
- Executive Summary: This is a concise overview of the entire report, highlighting key findings, conclusions, and recommendations. Think of it as the elevator pitch for your report.
- Introduction: This section sets the context by outlining the report’s purpose, scope, and methodology. It explains what the report will cover and who the intended audience is.
- Body: This is the heart of the report, presenting the actual data and analysis. It may include charts, graphs, and tables to visualize trends and patterns.
- Analysis and Interpretation: This section dives deeper into the meaning behind the data. It explains what the data reveals, identifies key trends and issues, and interprets their significance for the company.
- Conclusion and Recommendations: This section summarizes the key takeaways from the analysis and presents actionable recommendations based on the findings. It outlines a clear path for moving forward based on the insights uncovered.
Executive Summary
This part of the business report gives you the chance to explain the essence of your report. Therefore, the following are what you should include in it:
- A concise restatement of the report’s purpose: Briefly explain what the report aims to achieve and the specific business problem it addresses.
- Key findings: Highlight the most important insights gleaned from the data analysis. Focus on the information most critical for decision-making.
- Major conclusions: Summarize the overall picture painted by the data. Did you achieve your goals? Are there any unexpected trends or challenges?
- Actionable recommendations: Briefly outline the most important steps the company should take based on the report’s findings.
Introduction
This part of your business report sets the stage for your analysis. Below is what you should infuse into the introduction:
- Background information: Briefly explain the context surrounding the report. What prompted this analysis? What specific questions are you trying to answer?
- Scope of the report: Define the boundaries of your analysis. What time period or data sets are you focusing on? Are there any limitations to consider?
- Methodology: Briefly explain how you conducted the analysis. What techniques or tools did you use? This helps build trust in your findings.
- Target audience: Who is this report intended for? Tailor the language and level of detail accordingly.
Body
The Body is the workhorse of your report. Here’s where you present the data and your analysis in detail:
- Organize by topic: Divide the Body into clear sections based on the different aspects you’re analyzing (e.g., sales trends, marketing performance, customer satisfaction).
- Data visualization: Use charts, graphs, and tables effectively to present complex data in an easily digestible format.
- Data commentary: Don’t just present data; explain it! Highlight key trends, patterns, and outliers.
related article: Creative Ideas that Can Ignite Innovation in Your Business Strategies
Analysis and Interpretation
This part of your report goes beyond just showing the data; it’s about making it meaningful. Here’s how to approach this critical section:
- Explain the “why” behind the data: What do the trends and patterns tell you about the company’s performance?
- Connect data points: Identify how different metrics relate to each other. For example, how do marketing efforts impact sales figures?
- Identify strengths and weaknesses: Based on the analysis, what areas is your company excelling in? Are there any areas that need improvement?
Conclusion and Recommendations
Here’s where you tie everything together and provide a clear path forward:
- Restate key findings: Briefly summarize the most important takeaways from the analysis.
- Recommendations for action: Based on your findings, present specific, actionable steps the company should take to capitalize on opportunities or address challenges.
- Future considerations: Are there any further analyses or investigations recommended?
What is the Proper Format for a Business Report?
Each section on the business report has a specific purpose, and together they create a clear and functional space for presenting information. Now, let’s explore the proper format for a business report, dissecting each and its significance:
- Title Page: This is the first impression, so make it count! The Title Page should include:
i) Report title: A clear and concise title that accurately reflects the report’s content
ii) Author(s): Who prepared the report? Include names and titles
iii) Date: When was the report submitted?
iv) Company Logo (Optional): Adds a professional touch - Table of Contents (For Lengthy Reports): If your report is extensive, a Table of Contents acts as a roadmap, allowing readers to navigate quickly to specific sections.
- Executive Summary: As discussed earlier, this is the condensed version of your report, highlighting key findings and recommendations.
- Introduction: This section sets the stage, providing background information, report scope, methodology, and target audience.
- Body: The heart of the report, presenting data and analysis in detail, organized by topic with clear headings and effective data visualization.
- Analysis and Interpretation: This section goes beyond data presentation, explaining the “why” behind the trends and patterns, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and connecting data points to paint a holistic picture.
- Conclusion and Recommendations: Here, you summarize key findings and present actionable recommendations for moving forward.
- Appendix (Optional): Use the Appendix to include any supplementary information that might be too detailed for the main body, such as raw data tables, detailed calculations, or lengthy methodological explanations.
Read this: Effective Strategies on How to Do the Work and Achieving Business Goals
Bringing Data to Life: Unveiling Actionable Insights from Business Reports
Did you know that without the right approach, your business report can feel like dusty old maps leading nowhere? Now that you know, let’s take a close look at the keys that can help transform your business. By following these strategies, you’ll transform from a passive report reader to an active data detective.
Here are practical strategies to help you achieve this:
Ask the Right Questions
Before diving into the data, define your goals. What are you trying to learn from this report? Are you looking to improve sales conversion rates, boost customer satisfaction, or identify areas for cost reduction? Having clear questions will guide your analysis and help you focus on the most relevant metrics.
Think Beyond the Numbers
Numbers are important, but they don’t tell the whole story. Look for the context behind the data. Consider external factors like industry trends, competitor activity, and economic conditions. How might these external forces be influencing your internal numbers?
Embrace Storytelling with Data
Data visualization is your friend! Charts, graphs, and infographics can transform complex data into easily digestible visuals that tell a compelling story. Use these tools to highlight trends, patterns, and outliers that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Leverage Benchmarking
Don’t exist in a vacuum. Compare your performance metrics to industry standards or competitor benchmarks. This will help you identify areas where you excel or fall short, allowing you to learn from best practices and refine your strategies.
Look for the “Why” Behind the Trends
Data trends are interesting, but understanding the “why” behind them is crucial. Is a decline in sales due to a seasonal dip or a shift in consumer preferences? Identifying the root causes empowers you to take targeted action.
Highlight Actionable Insights
Don’t just present problems; propose solutions! Based on your analysis, what specific actions can your company take to capitalize on its strengths, address weaknesses, and achieve its growth goals?
Prioritize Recommendations
Not all recommendations are created equal. Prioritize your suggestions based on their potential impact and feasibility. Focus on the most impactful and realistic actions to maximize the return on your analysis.
Foster Collaboration
Business reports aren’t meant to be solitary journeys. Share your findings and recommendations with key stakeholders in different departments. Encourage discussions and collaboration to develop the most effective action plan.
Track and Measure Progress
Don’t let your analysis gather dust on a shelf. Once you’ve implemented your recommendations, track and measure their impact. Are you moving closer to your goals? This ongoing process allows you to refine your strategies and continuously improve your business performance.
Scorecard on Business Report
This scorecard is designed to help you assess your understanding of the article and its potential to empower you to unlock growth in your business. Rate yourself on a scale of 1 (Not Confident) to 5 (Highly Confident) for each question.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a business report?
A business report is a formal document that presents information and analysis on a specific business issue or situation. It can be used to inform decision-making, track progress, or identify areas for improvement.
Why are business reports important?
Business reports offer valuable insights into a company’s performance, financial health, and market position. By analyzing these reports, businesses can make informed decisions about growth strategies, resource allocation, and operational efficiency.
Who reads business reports?
Business reports can be targeted towards various audiences, including internal stakeholders (e.g., executives, department heads), investors, creditors, and regulatory bodies.
How can I collaborate with others to maximize the value of business reports?
Share your findings and recommendations with key stakeholders. Encourage discussions and collaboration to develop the most effective action plan based on the insights gleaned from the report.
Conclusion
By wielding the tools of analysis and interpretation, you can transform dry numbers into a roadmap for growth. Ask the right questions, embrace data visualization, and prioritize actionable recommendations. Collaborate with your team and leverage ongoing measurement to maximize the value of these reports.
References
- Piktochart.com – What is a Business Report? Examples, Tips
- Datapine.com – Business Report Examples
- Indeed.com – How To Write a Formal Business Report

