Understanding your market is essential in business. Companies need to know how their products and brands are seen compared to their competitors. This insight helps make smart decisions that can lead to greater success. One helpful tool for visualizing this perception is the perceptual map. If you’re a business leader or marketer looking to gain a competitive edge, you’re in the right place.
Let’s say you’re launching a new product in a crowded market. Even with its unique features, you struggle to position it against well-known competitors.
By the end of this article, you will not only grasp the main purpose of a perceptual map but also learn how to create one effectively. You’ll find out when to use perceptual mapping and understand its limitations. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to use perceptual maps to make informed, strategic decisions that can improve your market position.
What is the Primary Purpose of a Perceptual Map?
A perceptual map, also known as a positioning map, is a tool that shows how consumers see different products or brands in the market. The main purpose of a perceptual map is to show the competitive landscape from the consumer’s viewpoint, highlighting where various brands or products stand based on chosen attributes.
Understanding Consumer Perception
At the core of a perceptual map is the way consumers perceive things. By placing brands or products on a simple two-dimensional grid, companies can see how consumers view them in relation to key factors like price, quality, reliability, and innovation. This visual tool helps businesses understand their market position better.
Identifying Market Opportunities
One big benefit of a perceptual map is that it can uncover market opportunities. For example, if a certain area of the map is empty, it might mean there’s a market gap. This gap could be a chance for a new product or a rebranding effort to meet needs that aren’t currently being met.
Competitive Analysis
Perceptual maps are also great for analyzing the competition. By seeing where your brand or product stands in relation to others, you can better understand your strengths and weaknesses. This insight can guide important decisions like product development, marketing strategies, and pricing.
Enhancing Communication
Perceptual maps are excellent for communicating complex market data in a clear and concise way. They help present information to stakeholders, aligning marketing and business strategies with how consumers see the market.
Visualizing Market Trends
Perceptual maps can also show market trends over time. By regularly updating the map, companies can track changes in consumer perception and adjust their strategies as needed. This ongoing analysis helps businesses stay relevant and competitive in a constantly changing market.
See: Examples of Integrity in Leadership: Lessons from Successful Leaders
How Can I Create a Perceptual Map?
Creating a perceptual map involves a series of straightforward steps, from gathering data to plotting it on a grid. Here’s a simplified, step-by-step guide to help you make an effective perceptual map for your market analysis. By following these steps, you’ll be able to create a perceptual map that provides valuable insights and helps you make informed business decisions.
1. Define Your Goal
Before you start creating a perceptual map, it’s crucial to define your goal. What do you hope to learn from this map? Are you aiming to understand how your brand is perceived, find market gaps, or compare your product with competitors? Knowing your goal will steer the whole process in the right direction.
2. Choose Key Attributes
Pick the key attributes that matter most to consumers in your market. These should be relevant to your product and play a role in influencing buying decisions. Common attributes include price, quality, reliability, innovation, and customer service.
3. Collect Data
Gather information on how consumers view your product and your competitors’ products based on the attributes you selected. You can collect this data through surveys, focus groups, or market research studies. Make sure you have enough data to get reliable insights.
4. Analyze the Data
Look at the data you’ve collected to understand how consumers see each product or brand in relation to the key attributes. This might involve using statistical methods like factor analysis or multidimensional scaling to simplify the data and find the most important factors.
5. Plot the Data
Once you’ve analyzed the data, plot it on a two-dimensional grid. Each axis will represent one of the key attributes. Position each product or brand on the grid according to how consumers perceive it concerning these attributes. For example, a high-quality but expensive product would be placed towards the upper right corner.
6. Interpret the Map
Examine the perceptual map to gain insights into the market. Look for groups of products that are perceived similarly, identify any gaps or opportunities, and see how your product stands in relation to competitors. Use these insights to guide your strategic decisions.
7. Keep It Updated
A perceptual map isn’t just a one-time tool. Update it regularly to reflect changes in consumer perceptions and market conditions. This ongoing analysis will help you stay ahead of the competition and adjust to changing market dynamics.
You Should Read This: How to Become an Entrepreneur and Start Your Business: An Expert Guide
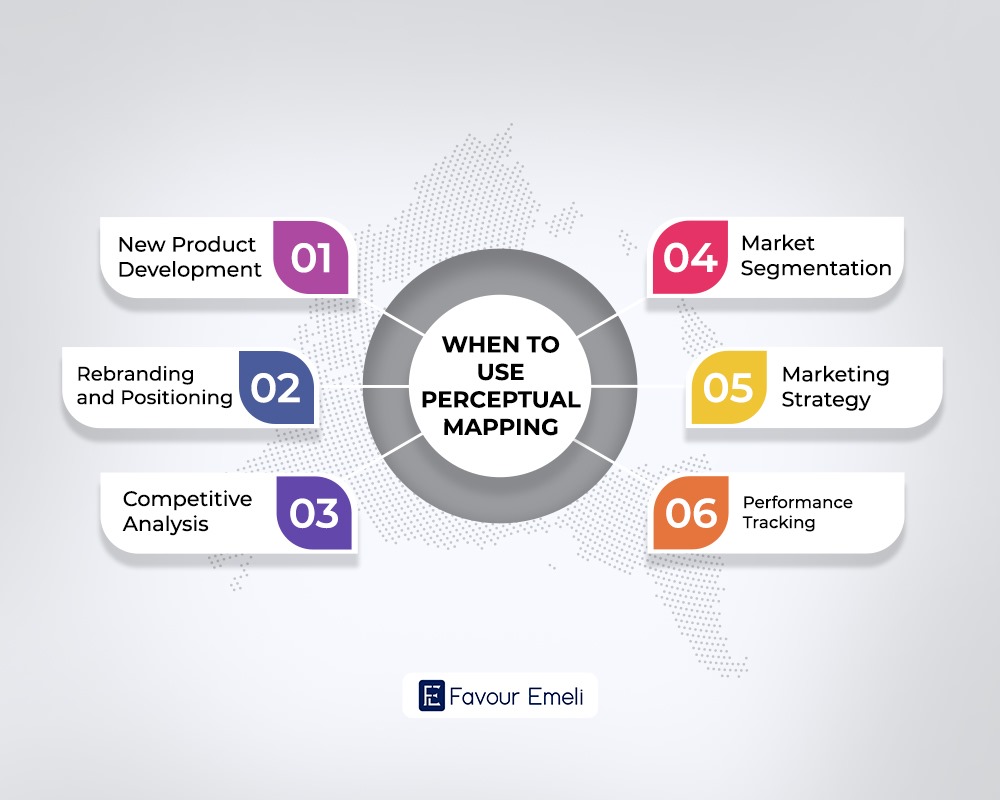
When to Use Perceptual Mapping?
Perceptual mapping is a flexible tool that can really boost your market analysis and strategic planning. Here’s how you can use it effectively:
- New Product Development: When you’re creating a new product, perceptual mapping can reveal market gaps. By spotting areas that current products don’t fully cover, you can design your new product to meet specific customer needs and preferences.
- Rebranding and Positioning: Thinking about rebranding or repositioning your product? A perceptual map can show you how customers currently see your brand and highlight chances to shift their perception. This insight helps you plan a rebranding strategy to achieve the desired market position.
- Competitive Analysis: Perceptual maps are great for competitive analysis. They let you see where your competitors stand and how your product stacks up. This comparison helps you pinpoint your strengths and weaknesses, shaping strategies to improve your market position.
- Market Segmentation: Perceptual mapping can help break down the market into different segments based on consumer perceptions and preferences. By understanding these segments, you can fine-tune your marketing strategies to better target specific groups.
- Marketing Strategy: A perceptual map can guide various parts of your marketing strategy, from product development to promotional activities. By grasping how consumers view your brand, you can craft marketing messages that resonate with your target audience and emphasize the most valued attributes.
- Performance Tracking: Track your brand or product performance over time with perceptual maps. Regularly updating the map with new data can show you how consumer perceptions are evolving and whether your strategies are working. This ongoing analysis keeps you aligned with market trends and customer needs.
What are the Weaknesses of Perceptual Maps?
While perceptual maps are very useful, they have some limitations you should keep in mind. Knowing these weaknesses can help you use perceptual maps better and avoid common mistakes.
- Picking the Right Attributes: Choosing the attributes for a perceptual map can be subjective. If you don’t pick attributes that really matter to consumers, the map won’t give you valuable insights. It’s important to choose attributes that truly reflect what consumers think is important.
- Collecting Reliable Data: Getting accurate data for your perceptual map can be tough. Surveys and focus groups depend on what people say, which can be biased or influenced by other factors. Make sure to use strong data collection methods and have a large, representative sample.
- Simplifying Too Much: Perceptual maps boil down complex consumer perceptions into two dimensions. This simplification can overlook important details and factors that affect consumer choices. While perceptual maps are helpful, you should also use other market analysis tools to get a fuller picture.
- Changing Market Conditions: Markets change quickly, and consumer perceptions can shift rapidly. A perceptual map is just a snapshot in time, and if you don’t update it regularly, it can become outdated. It’s essential to keep your map current by revisiting and updating it often.
- Interpreting the Map: Understanding a perceptual map can be tricky, especially if the data points are close together. You need to analyze the data carefully and be able to draw meaningful conclusions from the visual representation.
- Limited Dimensions: Perceptual maps usually show only two dimensions (attributes), which may not capture the full complexity of consumer perceptions. Although some methods allow for three-dimensional maps, these can be harder to understand and use effectively.
You may need to read this: 5 Ways to Deal with Disappointment in Business
Scorecard on Perceptual Map (Pdf.)
Below are scorecard questions to help your understanding of a perceptual map and the application of it.
FAQs on Perceptual Map
What is a perceptual map?
A perceptual map is a visual tool used in market analysis to display the perceptions of customers or potential customers about different brands or products. It typically positions products on a two-dimensional grid based on key attributes that are important to consumers.
How do I choose the attributes for my perceptual map?
Selecting the right attributes is crucial for an effective perceptual map. You should choose attributes that are most relevant to consumer decision-making in your market. This can be done through market research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
What data do I need to create a perceptual map?
To create a perceptual map, you need data on consumer perceptions of the attributes you’ve chosen. This data can be gathered through surveys where consumers rate products or brands based on these attributes. Ensure your sample size is large and representative of your target market.
Can perceptual maps show more than two attributes?
While traditional perceptual maps are two-dimensional, it’s possible to create three-dimensional maps to include a third attribute. However, these can be harder to interpret. Advanced statistical techniques like Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) can also help visualize more attributes.
Conclusion
Perceptual maps are super helpful for market analysis because they show you how consumers see your brand and your competitors. By understanding why they’re important, learning how to make them, knowing when to use them, and recognizing their limitations, you can use perceptual maps to make smart decisions for your business. Keep your maps updated and use them along with other tools to get a full picture of your market. This way, you’ll be ready to handle the competition and position your brand or product successfully.